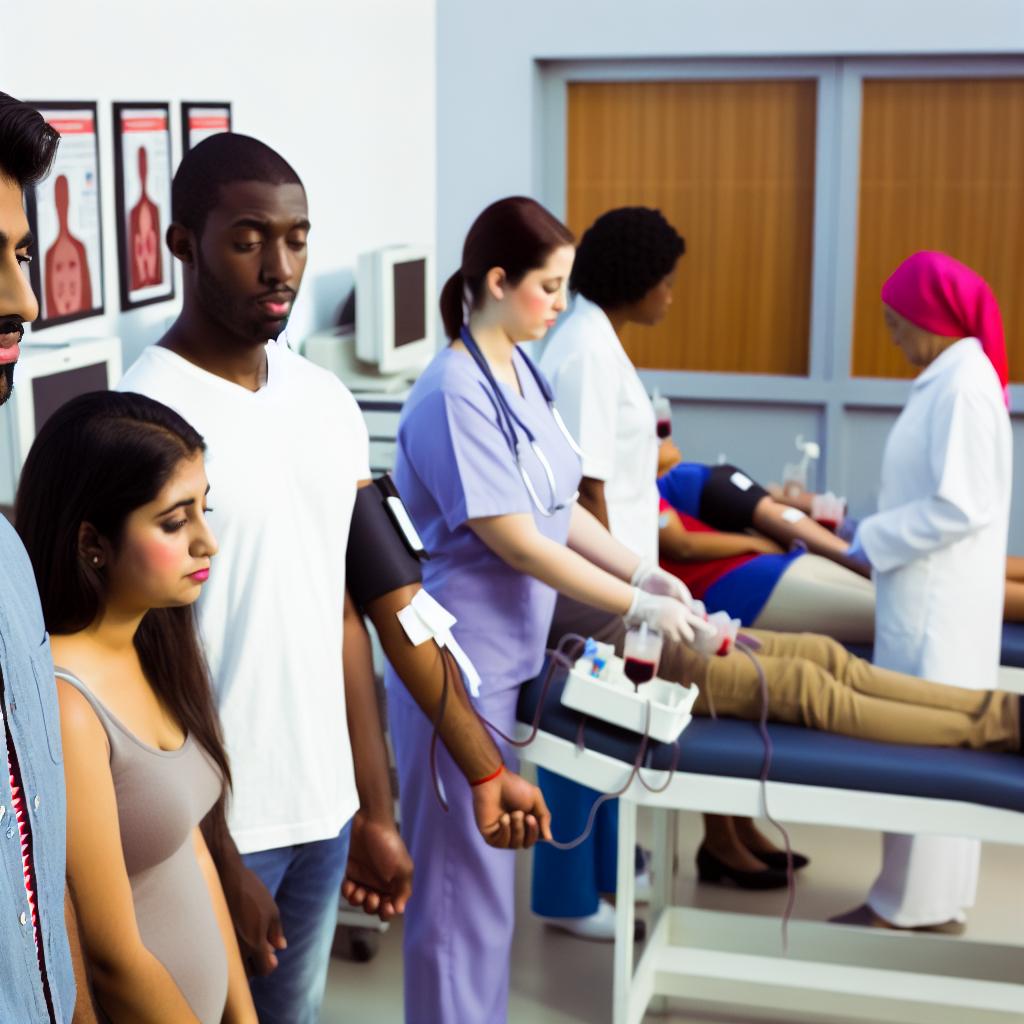
Introduction to Blood Donation
Blood donation is a crucial medical procedure that involves voluntarily giving blood to save lives and improve health outcomes. It plays an essential role in healthcare and is a key component during emergency situations.
The Importance of Blood Donation
Blood is a vital resource in healthcare. It is required for various medical conditions, including surgeries, cancer treatments, chronic illnesses, and traumatic injuries. The demand for blood is ever-present because it cannot be manufactured artificially and can only be provided by donors.
Blood Donation in Emergencies
In emergency situations, such as natural disasters, accidents, or conflicts, the need for blood escalates significantly. These situations often lead to an increase in injuries and surgeries, which in turn creates a surge in blood demand.
Natural Disasters and Blood Supply
Natural disasters like earthquakes, hurricanes, and floods can significantly disrupt blood supply chains. Infrastructure damage may hinder the collection, testing, and distribution of blood. Thus, maintaining a readily available supply of blood is essential for immediate response. National and international blood services often mobilize to manage and distribute blood resources in such scenarios.
Role in Trauma and Accidents
In trauma cases or large-scale accidents, the immediate availability of blood can mean the difference between life and death. Trauma injuries typically result in extensive blood loss, requiring urgent blood transfusions. Fire departments, emergency medical services, and hospitals rely heavily on blood banks to treat victims timely and effectively.
Blood Typing and Compatibility
Blood donation involves understanding blood types and their compatibility. The major blood groups are A, B, AB, and O, each of which can be Rh-positive or Rh-negative. O-negative blood is often referred to as the universal donor type because it can be transfused to patients of any blood type. This makes O-negative donations particularly valuable in emergencies when time constraints may prevent blood typing and cross-matching.
Encouraging Regular Donations
To ensure an adequate blood supply during emergencies, it is crucial to promote regular and voluntary blood donations. Public awareness campaigns, community drives, and educational initiatives are vital in encouraging people to donate frequently. For more information on blood donation and to find a donation center near you, please visit American Red Cross.
The Process of Blood Donation
Understanding the process of blood donation can help demystify it and encourage participation. When a donor arrives at a blood donation center, they undergo a registration process where their details are recorded. A brief health screening follows, which involves checking the individual’s vital signs and hemoglobin levels.
Once the donor is deemed fit to donate, the actual blood collection begins. The donor is comfortably seated and a sterile needle is used to draw blood. This process typically takes about 10 minutes, during which approximately one pint of blood is collected. After donation, the donor is advised to rest briefly and is offered refreshments to help restore their energy levels.
Post-Donation Care and Impact
After donating blood, it is crucial for donors to follow post-donation care instructions to ensure their well-being. This includes staying hydrated, avoiding strenuous physical activities, and maintaining a balanced diet for the next 24-48 hours. Donors often experience a sense of fulfillment knowing their contribution can potentially save lives.
The impact of such donations is profound. Every donation can help save up to three lives, thanks to the different components of blood: red cells, platelets, and plasma. These components can be separated and used to treat various medical conditions, making every donation significant.
Global Perspectives on Blood Donation
Blood donation practices and requirements vary across countries due to differences in healthcare systems and cultural perceptions. For instance, some countries may have more rigorous screening processes or eligibility criteria based on prevalent health issues. International cooperation among blood donation organizations is crucial for meeting global blood needs, especially during widespread crises.
Technological Advancements in Blood Donation
The field of blood donation has benefitted from advancements in technology, improving the efficiency and safety of the process. Innovations such as improved blood storage solutions, better testing methods for infectious diseases, and automated donation machines have enhanced the ability to store and distribute safe blood more effectively.
Moreover, digital platforms and mobile applications have made it easier for potential donors to find donation centers, schedule appointments, and receive reminders. These tools help maintain a steady flow of donations and streamline blood bank operations.
Future Directions in Blood Donation
As healthcare needs evolve, so does the landscape of blood donation. Future directions include exploring synthetic blood alternatives, which aim to supplement natural blood supply and potentially eliminate shortages. However, research in this area is ongoing and has yet to reach clinical application.
Additionally, efforts are being made to broaden donor eligibility, ensuring an inclusive approach that respects diversity while maintaining safety. Addressing factors such as lifestyle, travel history, and health status continue to shape the criteria for donation eligibility.
Conclusion
Blood donation is an indispensable part of emergency healthcare. It saves lives daily and becomes even more critical during crises. By understanding the importance of blood donation and its logistics, individuals and communities can contribute to bolstering the overall resilience of healthcare systems in times of need. Regular donations ensure a steady supply of blood to meet both everyday needs and emergency situations. As technology and practices continue to advance, the blood donation process will likely become even more efficient and far-reaching, ultimately saving more lives around the globe.